Pillars of Creation Webb
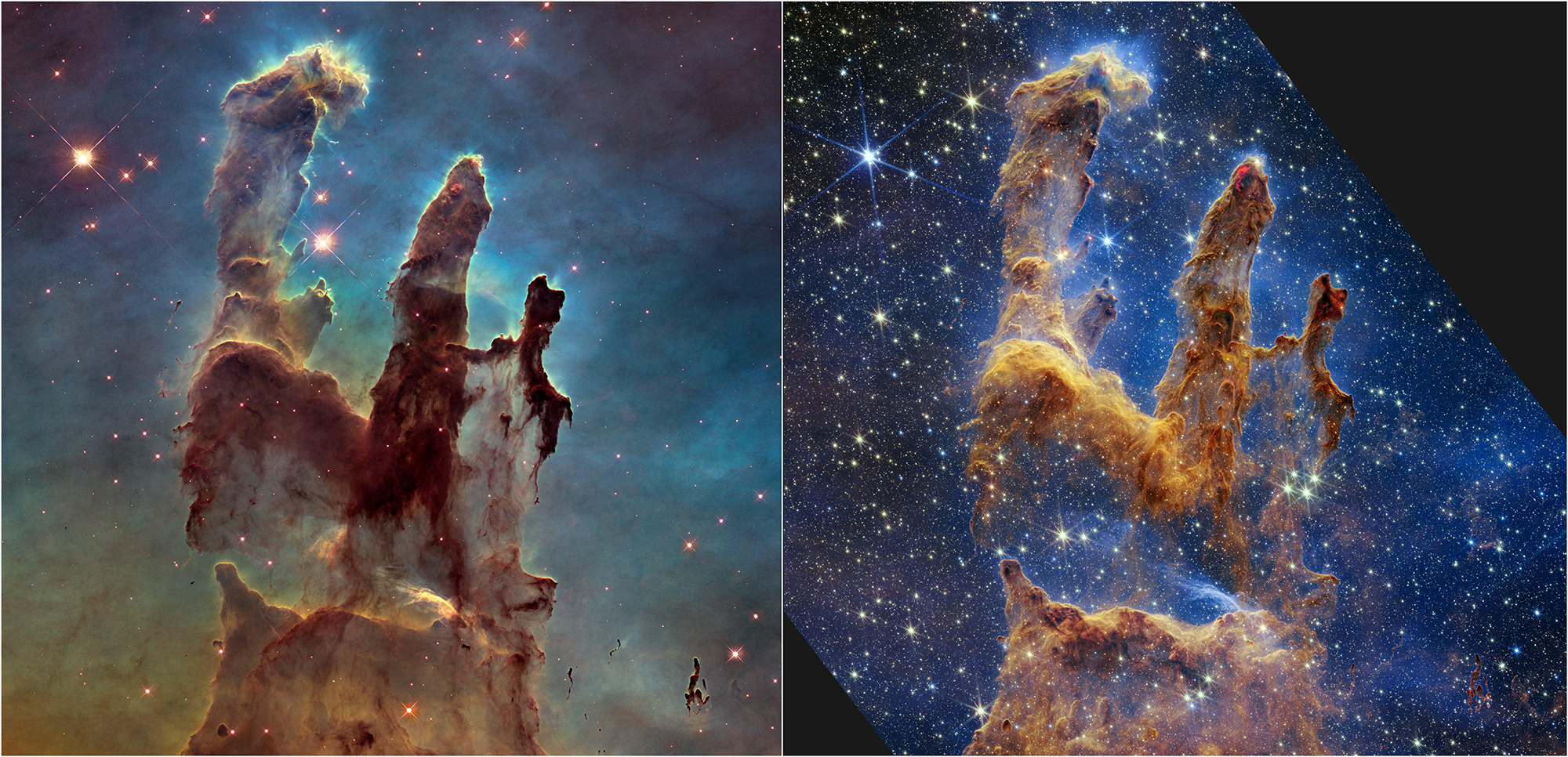

NASA's Hubble Space Telescope made the Pillars of Creation famous with its first image in 1995, but revisited the scene in 2014 to reveal a sharper, wider view in visible light, shown above at left.
A new, near-infrared-light view from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, at right, helps us peer through more of the dust in this star-forming region. The thick, dusty brown pillars are no longer as opaque and many more red stars that are still forming come into view.
While the pillars of gas and dust seem darker and less penetrable in Hubble’s view, they appear more diaphanous in Webb’s.
The background of this Hubble image is like a sunrise, beginning in yellows at the bottom, before transitioning to light green and deeper blues at the top. These colors highlight the thickness of the dust all around the pillars, which obscures many more stars in the overall region.
In contrast, the background light in Webb’s image appears in blue hues, which highlights the hydrogen atoms, and reveals an abundance of stars spread across the scene. By penetrating the dusty pillars, Webb also allows us to identify stars that have recently – or are about to – burst free. Near-infrared light can penetrate thick dust clouds, allowing us to learn so much more about this incredible scene.
Both views show us what is happening locally. Although Hubble highlights many more thick layers of dust and Webb shows more of the stars, neither shows us the deeper universe. Dust blocks the view in Hubble’s image, but the interstellar medium plays a major role in Webb’s. It acts like thick smoke or fog, preventing us from peering into the deeper universe, where countless galaxies exist.
The pillars are a small region within the Eagle Nebula, a vast star-forming region 6,500 light-years from Earth.
https://webbtelescope.org/contents/media/images/2022/052/01GF423GBQSK6ANC89NTFJW8VM